Analyst firm BloombergNEF has cautioned that Australia requires around AU$2.4 trillion (US$1.6 trillion) investment to reach net zero, with solar PV and wind installations to reach 290GW by 2050.
The organisation’s latest New Energy Outlook: Australia cautions that the nation’s energy transition risks being stalled without an “urgent scale-up” of clean energy technologies, such as solar PV and wind generation, alongside complementary technologies, like energy storage in the form of batteries and pumped hydro.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Or continue reading this article for free
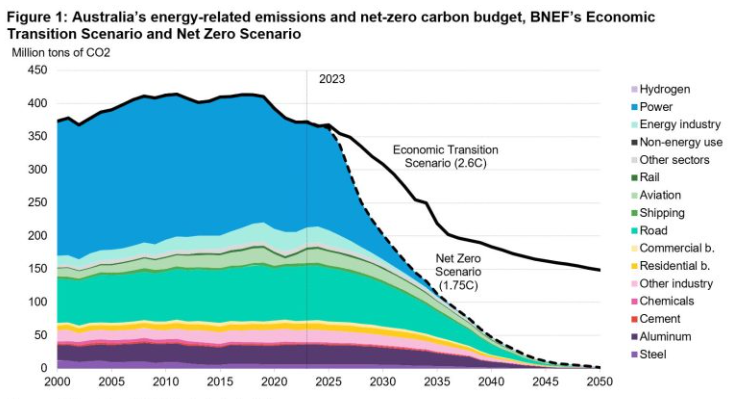
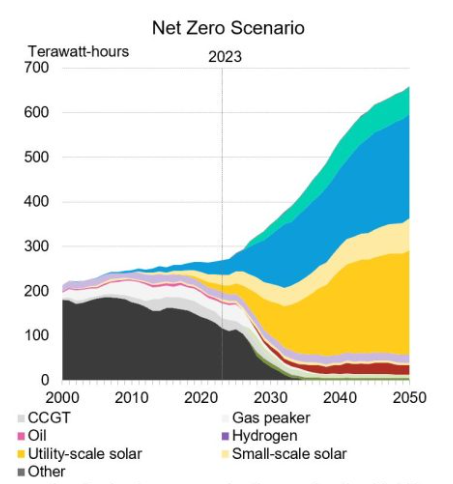
According to the report, there are immediate worries for the country to ensure it remains on a net zero trajectory. The power sector must rapidly decarbonise to stay on track, and thus, renewable energy capacity will need to grow by 135% compared to current levels before 2030, to 126GW. This is according to the report’s Net Zero Scenario.
Energy storage, in the form of pumped hydro and batteries, is expected to increase from around 3GW today to over 59GW by 2050.
Rapid deployment of both energy storage and renewable energy generation will be critical for net zero and offering grid stability, particularly with coal-fired generation plants expected to be withdrawn by 2038, according to the Australia Energy Market Operator (AEMO).
To help mitigate this, BloombergNEF emphasises that a greater uptake of renewable energy generation complemented with energy storage technologies will be required.
Leonard Quong, head of BloombergNEF in Australia, outlined that the move to a decarbonised power system will be “essential to cost-effectively reducing carbon emissions”.
“Australia’s window to stay on a well-below-two-degree pathway is closing, fast. Rapidly moving to a clean power system based on wind, solar and storage will be essential to cost-effectively reduce carbon emissions in line with our existing decarbonisation targets – but the heavy lifting must be done this decade. A low-carbon power sector will also serve as a bedrock for future emissions reduction efforts in other areas of the economy in the years to come,” Quong stated.
Australia can also not allow for any further carbon emissions growth in any sector if the country is to reach net zero by mid-century, with the report stating that the country’s emissions from power, transport, industry and buildings sectors “have already peaked”, and should now begin rapidly falling depending on the various technology pathways available for them to decarbonise.
Need for electrification could see support for emerging technologies
Tushna Antia, BloombergNEF Australia associate, highlights that the economic prospect for Australia’s wind and solar industries represents an “AU$213 billion opportunity by 2050”, but there’s no guarantee it will be fulfilled.
“Australia’s abundance of world-leading wind and solar resources gives us an advantage in decarbonisation, and combined they represent a AU$213 billion investment opportunity by 2050. But getting there won’t be easy, and we will need flexible demand from smart electric vehicle charging and hydrogen electrolysers, along with battery storage, flexible generators, and investment in the power network,” Antia said.
Indeed, various other technologies outside of renewable energy generation and energy storage are all expected to play their own parts in the push towards net zero. Hydrogen, as mentioned by Antia, could be a further complementary technology to the energy transition, especially with its potential to decarbonise hard-to-abate sectors such as steel production. Recently, the clean energy carrier has been used in Western Australia to help decarbonise a Fortescue mining operation to produce green metals, something that could lead to a lucrative export market.
Increased electrification in hard-to-abate sectors could also mean a greater need to scale energy generation in Australia. Although decarbonisation of the power sector could account for around 54% of emissions avoided by 2050, the electrification of end-use sectors, including road transport, buildings and industry, accounts for a further 21% of avoided emissions.
Sahaj Sood, BloombergNEF Australia senior associate, said that pioneering new clean and low-carbon technologies such as hydrogen, biofuels and carbon capture will be “essential for Australia to reach net zero”.
“While questions still remain about their reliability, acceptability, and scalability – if they aren’t able to be used, emission reductions will have to come from somewhere else in the economy, and likely from more expensive solutions,” Sood added.







