A study from the Fraunhofer Institute for Energy Systems (ISE) in Germany has detected reliability issues in tunnel oxide passivated contact (TOPCon) solar cells.
The study conducted an analysis of 20 TOPCon PV module types from a wide range of manufacturers, using a range of electrical characterisation and accelerated aging assessments. It detected some failure modes that appear to be noncritical, such as light- and temperature-induced degradation (LeTID).
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Or continue reading this article for free
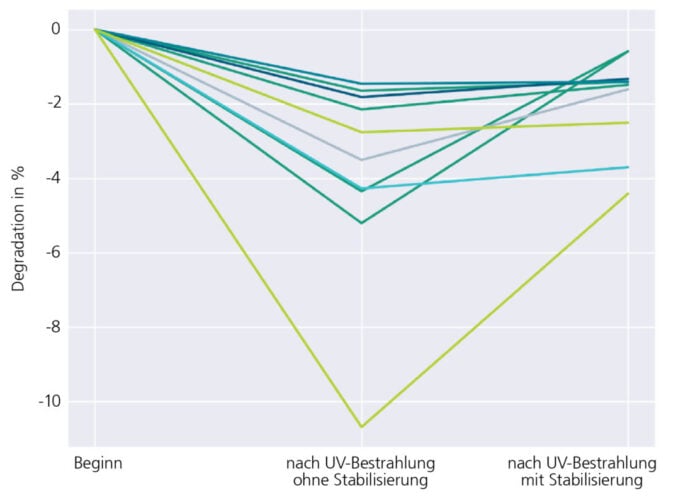
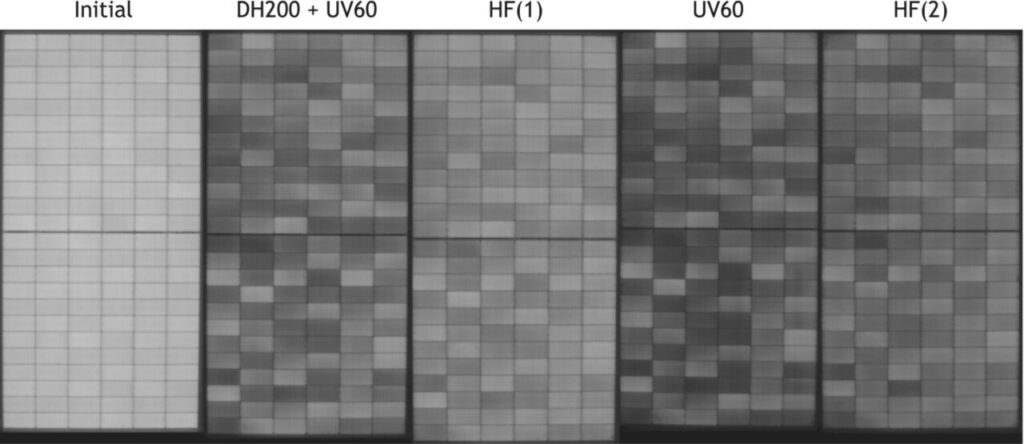
However, Fraunhofer ISE’s study, which was recently published in Progress in Photovoltaics, uncovered critical degradation effects caused by moisture ingress and UV irradiation in accelerated aging. Moisture-related degradation issues were due to the sensitivity of current from metalisation pastes, which could be mitigated in future module generations.
The combined test sequence of UV/HF showed a “W-pattern” of significant degradation, which was followed by partial recovery, wrote the study’s authors. Other investigations showed that the degradation was influenced by the mode of operation – short or open circuit – whereas recovery was influenced by temperature, current injection and most likely light soaking, although further testing work is being completed on this latter factor.
“During UV exposure, a novel degradation pattern was observed during the indoor tests, showing severe losses (up to -12% after 120 kWh/m2), followed by recovery after humidity freeze testing, which may influence outdoor performance and the outcomes of certification tests (IEC 61730-2, Sequence B),” wrote the authors of the study.

Despite that critical degradation effect, the study showed that TOPCon cell technology performed better than passivated emitter and rear contact (PERC) in terms of efficiency, bifaciality and temperature coefficient. Similar to more recent PERC generations, TOPCon modules have not shown increased sensitivity towards light- and potential-induced degredation, or LeTID.
In a guest blog published earlier this year on PV Tech, George Touloupas, senior director at the Clean Energy Associates (CEA) and Brian Hansen, director of supply chain at CEA, wrote about some of the technological differences between PERC and TOPCon technology.
To celebrate its tenth anniversary this year, PV Tech Power revisited an article it covered in the first issue relating to PV module quality and how, a decade and a shift from p-type to n-type technology later, the industry was doing in that aspect. The article can be read online here (Premium access).
“We recommend conducting focused tests on specific module types (tailored to the BOM if possible), emphasising DH, potential-induced degradation, UV and mechanical load, before purchasing substantial quantities of TOPCon modules from the current market. Due to the relative recent appearance of TOPCon-based modules on the market, we expect the reliability characteristics to change and improve during the next months, which could also change the best practice for qualification testing,” concluded the study.