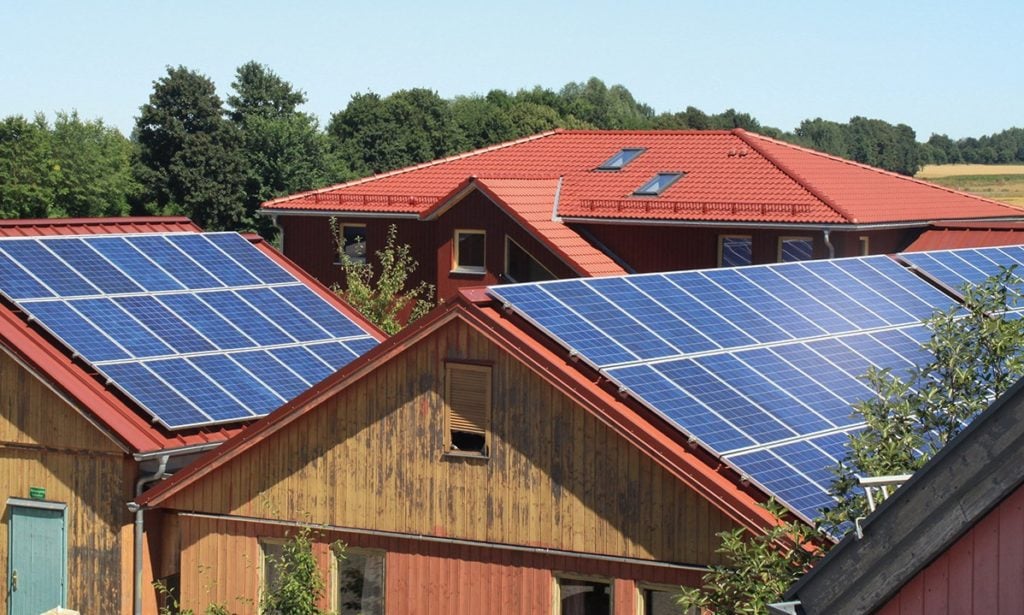
There has been an increase in the share of PV systems in Germany that have an eastern and western orientation, according to new findings from Fraunhofer ISE.
Through a study into registered PV installations in the country, the solar research institute found that between 2000 and 2019, the share of east-facing systems increased from 1% to 7%, west-facing projects rose from 3% to 9% and east-west orientations increased from 1% to 6%.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Or continue reading this article for free
The percentage of systems that are not south facing has increased from 39% to 58% in the last 20 years, which can result in yield losses, the amount of which depends significantly on inclination angles.
According to Fraunhofer ISE, if a system has an optimal inclination angle, the yield loss can be 5 – 10%. However, yields can be up to 50% lower for systems that are orientated towards the north.
The research found that more PV plants in Germany are being installed with smaller tilt angles. Between 2000 and 2009, the annual share of PV systems with a tilt angle of less than 20 degrees averaged 10%; from 2010 to 2019, the percentage increased to an average of 19%.
Plants with tilt angles between 20 and 40 degrees accounted for an average share of 63% between 2000 and 2009, which fell to 54% between 2010 and 2019.
Fraunhofer ISE also revealed that about a quarter of newly installed plants in 2019 in Germany have no output limitation, while about 66% of plants are limited to a maximum grid feed-in of 70% of their output power.