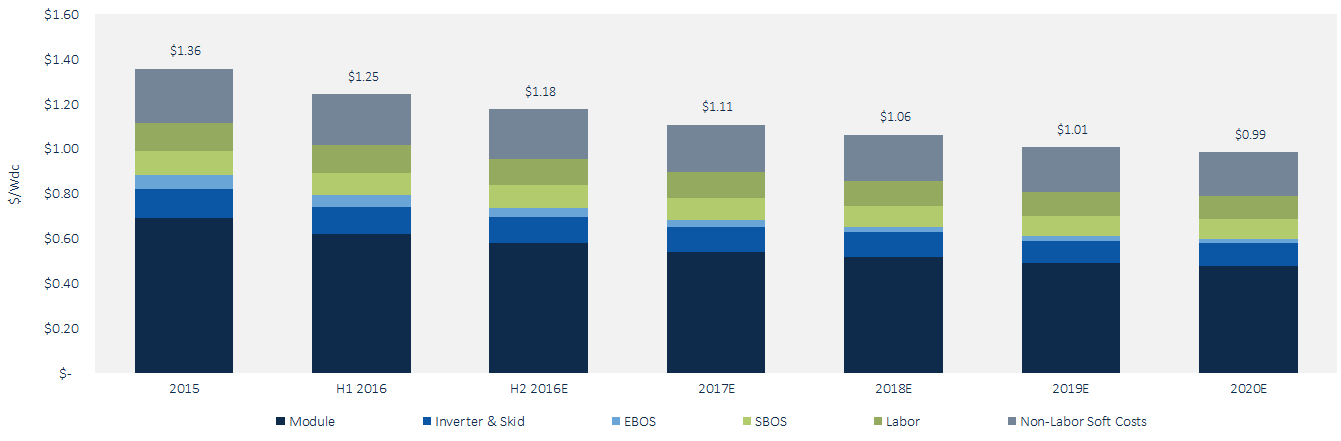
According to a new report from GTM Research, pricing for fixed-tilt ground mount PV systems are expected to hit US$0.99 per watt by 2020.
The report, “US Solar PV Price Brief H1 2016: Pricing, Breakdowns and Forecasts”, notes that this would fall in line with the Department of Energy’s ambitious SunShot target of US$1.00 per watt by the end of this decade.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Or continue reading this article for free
Currently, GTM Research estimates the price for a utility-scale fixed-tilt ground mount PV system to be around US$1.25 per watt today. Modules are responsible for half of the cost, additional hardware like inverters and balance of system components represent 22%, while the remaining 28% is comprised of soft costs.
The report adds that soft costs stand as both the biggest opportunity and the largest challenge for future cost reductions — especially in the residential and commercial market segments where prices are much higher than utility-scale segments.
Residential PV projects in the US averaged US$3.00 as of the first half of 2016. According to GTM, soft costs make up 64% of residential system costs today. Average US commercial solar prices just dipped below US$2 per watt, but the report adds that there are plenty of other opportunities when it comes to finding further cost reductions.
Ben Gallagher, GTM Research solar analyst and lead author of the report, said: “Commercial PV installers need to find more ways to shorten the length of the project cycle and de-risk aspects of the project cycle in order to substantially reduce origination and overhead costs.”







