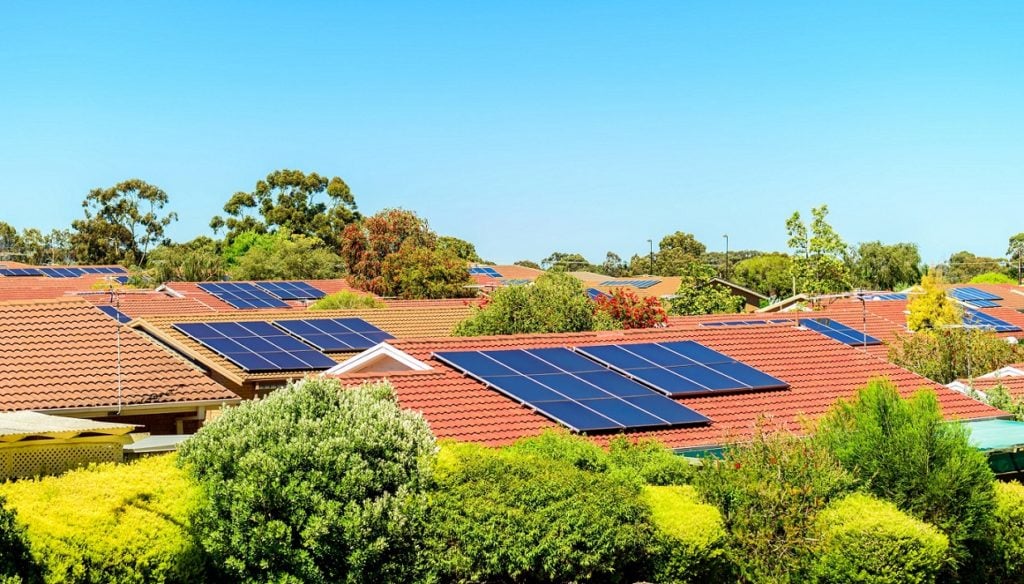
Wealthy renters in Australia are more likely to benefit from properties with solar power access with more than 90% of tenants in Australia lacking direct access, according to a study conducted by Macquarie University.
In the study based on data from the Australian Bureau of Statistics for over 17,000 renters surveyed between 2012 and 2020, the co-authors found that renters who benefitted from properties with solar power access could have their savings translated to more disposable income to spend on consumer items or investments.
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Or continue reading this article for free
“In some cases renters can save hundreds a year if not a thousand depending on electricity usage, that’s significant savings when things are tough,” said Rohan Best, one of the researchers of the study.
The researchers also said that net wealth was better for identifying solar-access inequality than other socio-economic variables such as income, welfare receipt, or education.
Looking forward, Best suggested several ways that the government can do to narrow the gap between renters who have access to solar panels and those who do not. For example, rebates could be higher for the least wealthy 20% of renters compared with wealthy renters who were often paying the highest amount of rent per month in more expensive suburbs.
“Targeting landlords may be the most effective mechanism for change. Incentives could help persuade them to install the panels and savings are then partly passed onto the tenant,” said Rohan.
Long leases could also be a solution. After securing long-term tenants, landlords may be more inclined to invest in solar panels and absorb the costs in a sustainable rent price schedule.
Australia is ramping up its energy mix. This year, renewables including solar, wind and hydropower accounted for about 30% of Australia’s electricity generation. As of 2022, Australia’s cumulative large-scale installed capacity stood at 6,487MW, increasing from 5,627MW in 2021.