Boosted by the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and tariff policies, the US has set off a boom in domestic PV manufacturing.
In addition to local manufacturers, others from Europe, India and the Middle East have also initiated plans to build plants in the US
Unlock unlimited access for 12 whole months of distinctive global analysis
Photovoltaics International is now included.
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Unlimited digital access to the PV Tech Power journal catalogue
- Unlimited digital access to the Photovoltaics International journal catalogue
- Access to more than 1,000 technical papers
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Or continue reading this article for free
According to the ‘US Solar Market Insights Report Q3 2024’ released by the Solar Energy Industry Association (SEIA) and analysts Wood Mackenzie, current PV manufacturing capacity in the US has exceeded 31GW, with Arizona, Nevada and Georgia becoming popular states for investment.
The module segment has become the most concentrated area in terms of investment and plant construction, with the IRA providing generous tax incentives for manufacturers, which have in turn given rise to new supply chain demands, with equipment, materials and services all emerging as prioritised items.
Against this backdrop, this year’s RE+ exhibition witnessed a new peak in the number of participating companies from the supply chain, with PV Tech sitting down for a conversation with leading Chinese equipment company Ningxia XN Automation.
Companies vying to adopt TOPCon and HJT, new breakthroughs in 0BB on key equipment
Founded in 1999, Ningxia XN Automation entered the PV industry in 2008, since then working closely with module manufacturers to overcome challenges associated with the evolution of module technology and earning a reputation for its innovative capabilities.
“Now considered a PV industry veteran, we have been producing module manufacturing equipment for sixteen years, and have been among the first to propose and enable many technological innovations. As a company, we never fear rapid technology upgrades. Our proven approach is to comprehensively evaluate new technology at an early stage, and then conduct in-depth research on the best technical solution to carry out effective equipment optimisation. We have always worked hand in hand with our customers to drive the industry forward,“ commented head of sales Xue Zhen.

The company’s main area of expertise is in sophisticated module manufacturing equipment, including automated welding stringers, auto bussing and layup machines, earning it a reputation for excellent product performance and reliability.
Among these products, the welding stringer is the core equipment for producing modules, and also the equipment that features state-of-the-art technology and has the highest value in terms of the module encapsulation line. Currently, the cost for a single gigawatt of welding stringers can exceed RMB20 million (US$2.8 million), accounting for around 35% of the total value of the equipment.
Based on the number of busbars required for different modules, welding stringers can be divided into three types: the MBB (multi-busbar), the SMBB (super multi-busbar) and the 0BB (0-busbar). Viewed from current market applications, with the emergence of new cell technologies such as TOPCon and HJT, the string welding process has begun to evolve from MBB to SMBB. The new 0BB generation has also begun to emerge.
As a state-of-the-art technology, 0BB does not use silver electrodes, but replaces them with a welding strip, which can be directly connected to fine busbars to collect current. While an MBB welding strip has a diameter of 0.3-0.4mm, the 0BB strip has a diameter of 0.2mm, which leads to less light obstruction and shorter current transmission distance, thereby reducing current loss and improving power generation efficiency. Given these advantages, many cell and module companies are ramping up their research and development (R&D) efforts to achieve this new technological breakthrough.
The accelerated pace of module busbar innovation has brought opportunities for welding stringer upgrades. With the increasing acceptance of 0BB by module leaders, Soochow Securities estimates that the 0BB market will reach nearly RMB3 billion (US$430 million) in 2025, with a combined annual growth rate (CAGR) of 285% from 2023 to 2025.
In response to the PV industry’s ever-urgent need for cost reduction and efficiency enhancement, XN Automation has launched its Integrated Film Covering (IFC) innovation, which is suitable for the stringing of 0BB solar cells. This technology utilises a low-temperature process to accurately press the wire onto the front and back sides of cells with a film in one go, forming a pre-connected string. The metallised combination of the wire and busbar is completed by a subsequent film covering process.
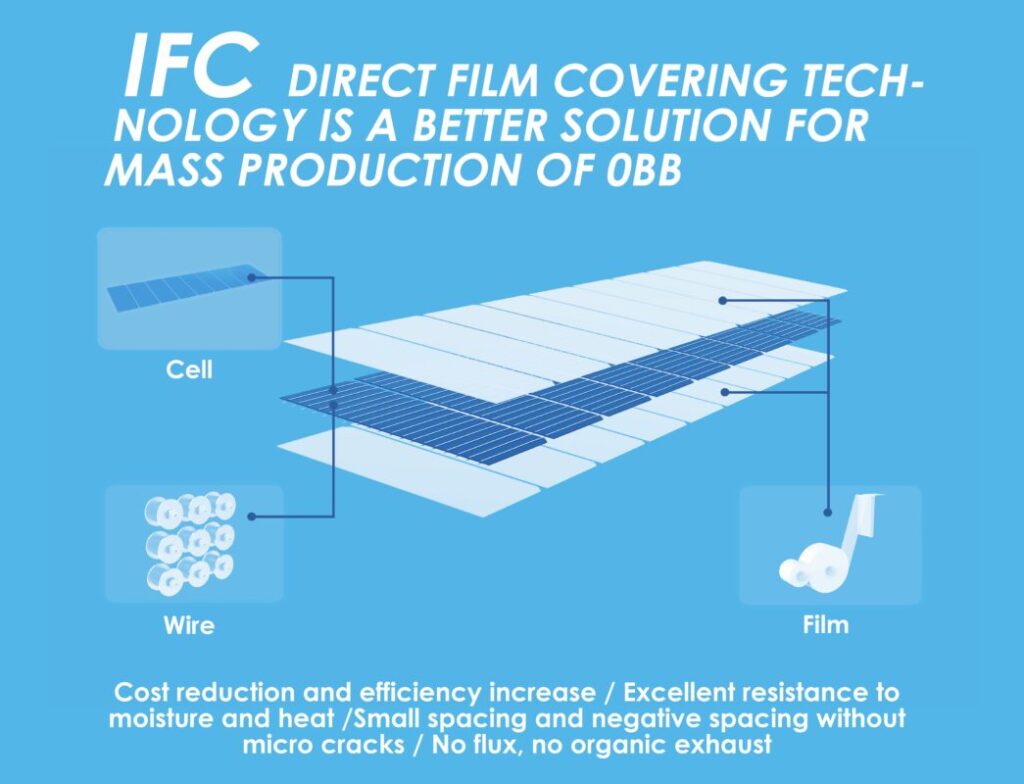
This revolutionary technology breakthrough not only greatly simplifies 0BB module production, but also significantly improves production efficiency and quality, enabling 0BB modules to achieve mass production, setting a new benchmark for the industry in cost reduction and efficiency enhancement.
Xue Zhen went on: “We have compared and verified processing schemes of 0BB stringing at an early stage. We have also taken into account the characteristics and needs of markets both at home and abroad. Later, in 2022, we first proposed the direct film covering technology. This technology does not require the use of flux agents throughout the entire process, which greatly reduces maintenance time for operators and improves the equipment’s operating efficiency. The simplified process also lowers the skill requirements for operators.”
Moving to low-temperature processing technology, this is more adaptable and suitable for the thinner HJT and TOPCon cells, being less sensitive to the thermal conditions of the equipment. Intermittent production can quickly reach full-capacity operation and the end product with this technology has higher output and a more aesthetically pleasing appearance. Based on these advantages, the company has developed CHJ40, an integrated film covering the stringer to safeguard mass production of 0BB modules.
Having been used in the industry for almost two years now, this advanced equipment has already achieved large-scale mass production for more than half a year. From initial testing to mass production, many indicators have exceeded expectations, with excellent mass production yields delivered.
“At the beginning, the technology was applied with HJT, but now it is coming to fruition with TOPCon. Our client CHINT was the first to use IFC to achieve mass production of 0BB TOPCon, and its 0BB modules received certification from TÜV Rheinland in October 2023,” Xue Zhen continued.
“After a comprehensive assessment, we believe that no matter whether HJT or TOPCon, direct film covering is a better solution for 0BB. What needs to be done now is to enable more customers to use this technology, so that its benefits can gradually be extended to the industry at large to enhance the competitiveness of our customers’ products.“
Business layout in the US on the path to globalisation
As one of the earliest companies engaged in the R&D and manufacturing of PV equipment, from 2008 to 2023, XN Automation has continually expanded its presence in the welding stringer market. Known for low breakage rates, low energy consumption and a high cost-performance ratio, its welding stringers have been supplied to many of the industry’s mainstream PV module companies.
“We always look to come up with different innovations, enabling PV companies and the industry in general to make forward-looking judgments. Such innovations are valuable assets for the entire industry,” commented general manager Wang Xiaoniu.
Not only serving Chinese manufacturers, the company was also among the first to enter the international market.
“We first began to receive overseas orders in 2013 and, at that time, we set up an overseas after-sales team. In 2016, we created an independent overseas sales team, which has served us very well over the intervening eight years.”
“The US, Mexico and Canada together account for about one-third of overseas customers, with European countries including Italy, Germany, France and Turkey accounting for another one-third, and the remaining one-third being distributed across Southeast Asian countries. The main products exported include regular welding stringers, layup and auto bussing machines and tape applicators,“ Xue Zhen added.
As of H1 2024, the company’s products had been shipped to some 30 countries and regions across the US, Europe and Asia.
“This year has been our first time to participate in the RE+ exhibition. Our products are already in operation at a number of American companies, including Silfab, Mission Solar, Heliene and SEG Solar. Canadian Solar’s US subsidiary uses our auto bussing machine, while Hanwha’s bases in the US, South Korea, Germany and Malaysia all use our full range of products.”

“We aim to provide further competitive products for the US market. The high labour costs here necessitate high levels of automation and extremely reliable equipment. We are currently strongly recommending CHJ40, the integrated film covering stringer, to our customers, together with the film covering string rework machine.”
“Compared with the domestic market, products for overseas markets have a certain lag, but it’s clear from what we’ve seen at this exhibition that the latest domestic technology can fully meet overseas demand. We will continue to promote these technologies, so that the simple manufacturing and green environmental protection offered by direct film covering can benefit more people as soon as possible.”







